Interact with Spatial data services using QGIS Desktop
In case you find a relevant spatial dataset in the LSC Catalog you will notice in the link section of the record if a downloadable file or a web service to the data is available and of which type it is. Various tools can be used to open these formats and web services. On this page we list methods on how to open a data service in QGIS.
QGIS is an open source desktop GIS application available for Windows, MacOX, Linux and Android. It supports a wide variety of spatial formats, spatial data services, digitisation tools and spatial processing tools. If you are not familiar with QGIS, follow the getting started tutorial first.
Visualize data using OGC:WMS
OGC:WMS is a standardized protocol to visualize data over the web. A WMS service typically provides access to one or more datasets (layers). For each layer one or more visual representations can be available.
To display a WMS layer in QGIS, Select from the menu Layer > Add Layer > Add WMS/WMTS Layer. This opens the Add layer panel.
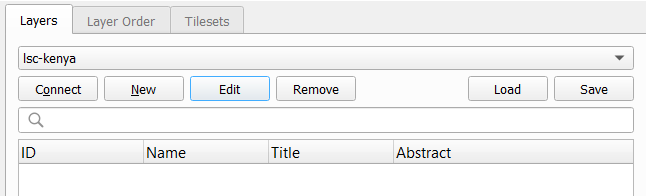
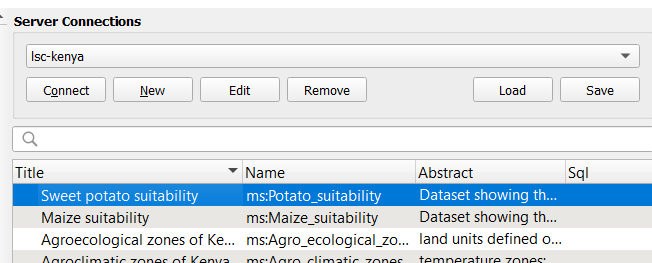
First we are adding a new service connection. Select the New button. Copy the url of the service from the catalogue result and paste it in the url field in QGIS. Provide a sensible name and save the connection.
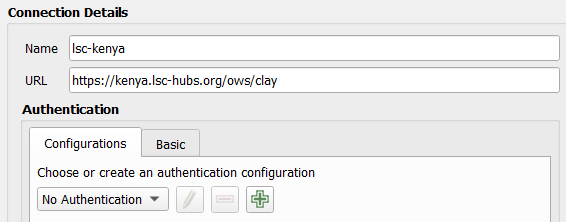
With the service selected, click the connect button and the layers which are available in the service are displayed
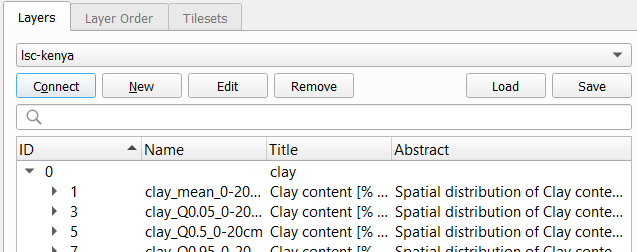
Select the relevant layer and click Add at the bottom of the panel. The Layer is now displayed on the map. If you don’t see it yet, right click the layer on the table of content and select Zoom to layer. If the layer still is not visible, verify the log panel of QGIS, to understand if communication errors have occured.
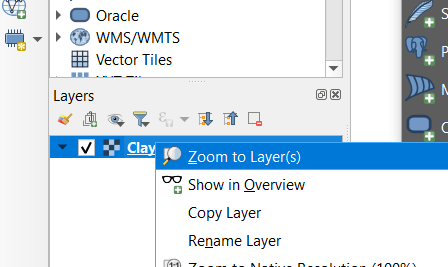
Understand that you can not select features, because the interaction with the service is based on images. You can however use the i tool to retrieve attribute information from pixels. A dedicated method on the service, called ‘getFeatureInfo’ is used.
Visualize and download vector data using OGC:WFS or OGCAPI:Features
OGC:WFS is a standardised protocol to share vector features over the web. OGCAPI:Features is a modern alternative to WFS, supported by some servers. Adding a WFS or Features layer to QGIS uses a similar procedure as adding a WMS layer. Select Layer > Add layer > Add WFS layer from the menu. Notice that only vector layers are shown, grid layers use the WCS protocol (see next paragraph).
Notice the build query button in the footer of the panel. This allows you to filter features on attribute value, for example pH < 5. Substantially less data will be retrieved, improving the performance.
With the layer added to the view, notice that the data has no styling, it acts as any other vector dataset. You can select features and even open the attribute table.
To extract a subset of the data, zoom to the area of interest, then right click the layer in the table of contents and select Export > Save Features As.
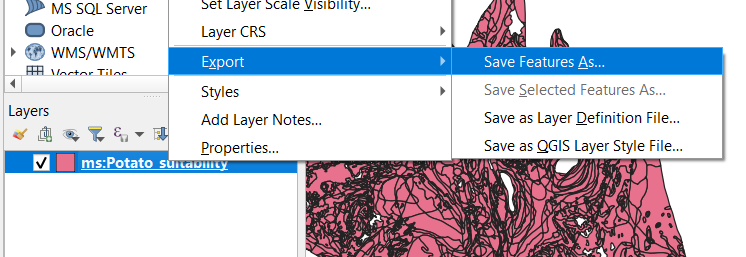
On the export panel, set the format, a file location and set the extent (current). Then select OK.
Visualize and download grid data using OGC:WCS
OGC:WCS retrieves subsets from a grid dataset. Adding a WCS layer to QGIS uses a similar procedure as adding a WFS layer. Select Layer > Add layer > Add WCS layer from the menu.
The WCS layer behaves like any grid layer in QGIS, you can retrieve the pixel value and run grid processes on the layer.
Exporting a grid for a region of interest works similar as WFS.
Alternatively, TerriaJS, if configured, offers the option to download a subset of a WCS coverage as TIFF file. Subsequently you can add the tiff file as a layer in QGIS.
Visualize and download observation data using Sensorthings API
Soil observation data is sometimes made available through Sensorthings API. In recent version of QGIS the Sensorthings API is supported, before a plugin was required. This article provides information on how to add a sensorthings service in QGIS. An example sensorthings API service with soil data is soilthings